
- #DATA BACKUP BEST PRACTICES MANUAL#
- #DATA BACKUP BEST PRACTICES FULL#
- #DATA BACKUP BEST PRACTICES PORTABLE#
#DATA BACKUP BEST PRACTICES MANUAL#
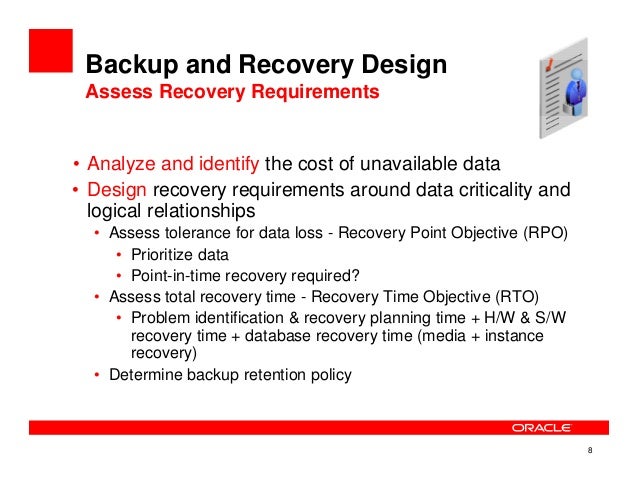
Operators should be able to build intelligent policies that are automated, are able to detect new applications on their own, and eliminate the hassle of manual updates. Developers should have self-service capabilities, and not be required to make code, packaging, toolchain, or deployment changes. A good cloud-native backup solution will provide operations teams with a streamlined workflow, while still meeting all requirements for compliance and monitoring. Your backup platform should not impact efficiency. It’s important to have the flexibility to restore all or parts of the application at a granular level. object storage, snapshots, etc.) and prepare the backup storage. The next step is to identify the backup data sources (i.e. Make sure you verify cluster dependencies, create new Kubernetes views of the data to be restored, and determine the compute infrastructure and Kubernetes cluster where recovery will be initiated. Adequate disaster recovery requires careful planning combined with the right tools for execution. It’s important that your backup solution can scale up automatically with changes to your application, and scale down to zero when not in use. Follow the 3-2-1 rule: keep at least three copies of the data stored on two different media, and one copy should be offsite. You must then determine how you’ll capture the application's data, and decide where to store it. A Kubernetes-native backup solution will automatically discover all the components running on the cluster, and treat the application as a unit of atomicity.
#DATA BACKUP BEST PRACTICES FULL#
A full application capture, including all components, resources, filters and labels is a necessary step to ensuring a reliable backup. Attempting to use traditional backup methods puts you at risk of data loss or corruption, because legacy solutions fail to capture the application as a whole - including all stateful and stateless components. Kubernetes is application-centric, so a Kubernetes-native backup is essential.

Here are six best practices you should follow when implementing a Kubernetes backup solution: With a proper native backup strategy in place, you’ll feel more confident when utilizing the powerful, yet complex Kubernetes platform. Implementing Kubernetes-native backup for your applications is critical to protect your data in the event of an accident, system failure or even a deliberate attack.

Some of the features that make Kubernetes a powerful application deployment environment can also create new challenges when it comes to managing and protecting your data. Yet despite offering numerous advantages over on-premises systems, moving to the cloud can sometimes be a double-edged sword.
#DATA BACKUP BEST PRACTICES PORTABLE#
The adoption of cloud-native development practices, particularly with Kubernetes, is rapidly accelerating as companies shift from last-gen tech to the far more reliable, scalable and portable environment that the cloud provides.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
